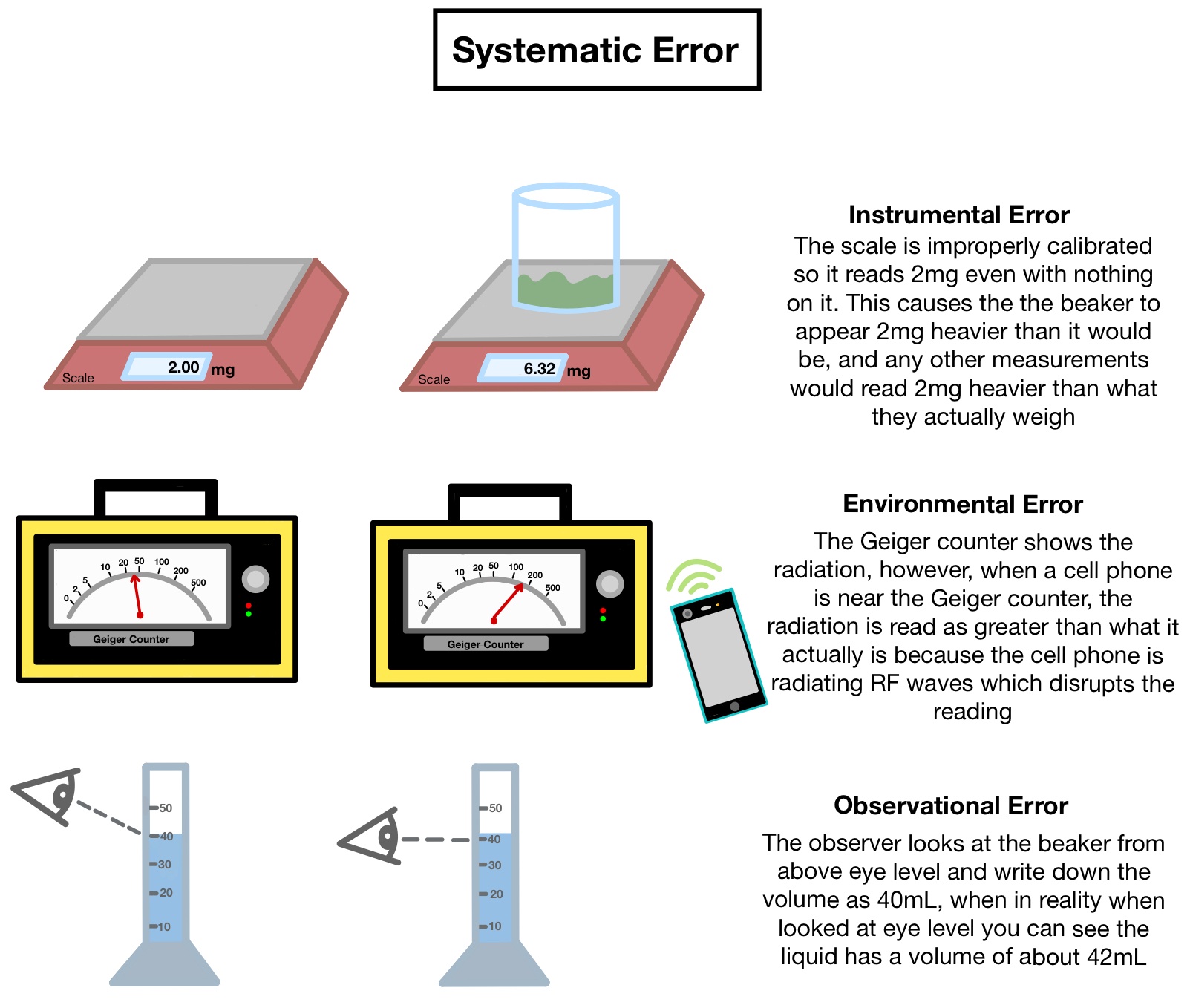
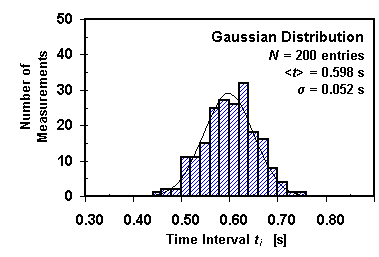
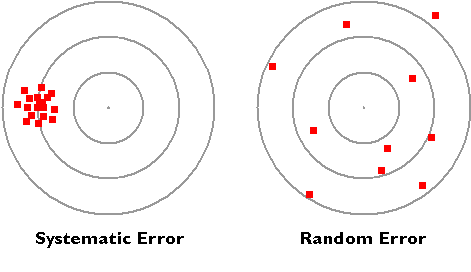
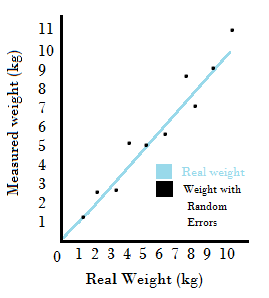
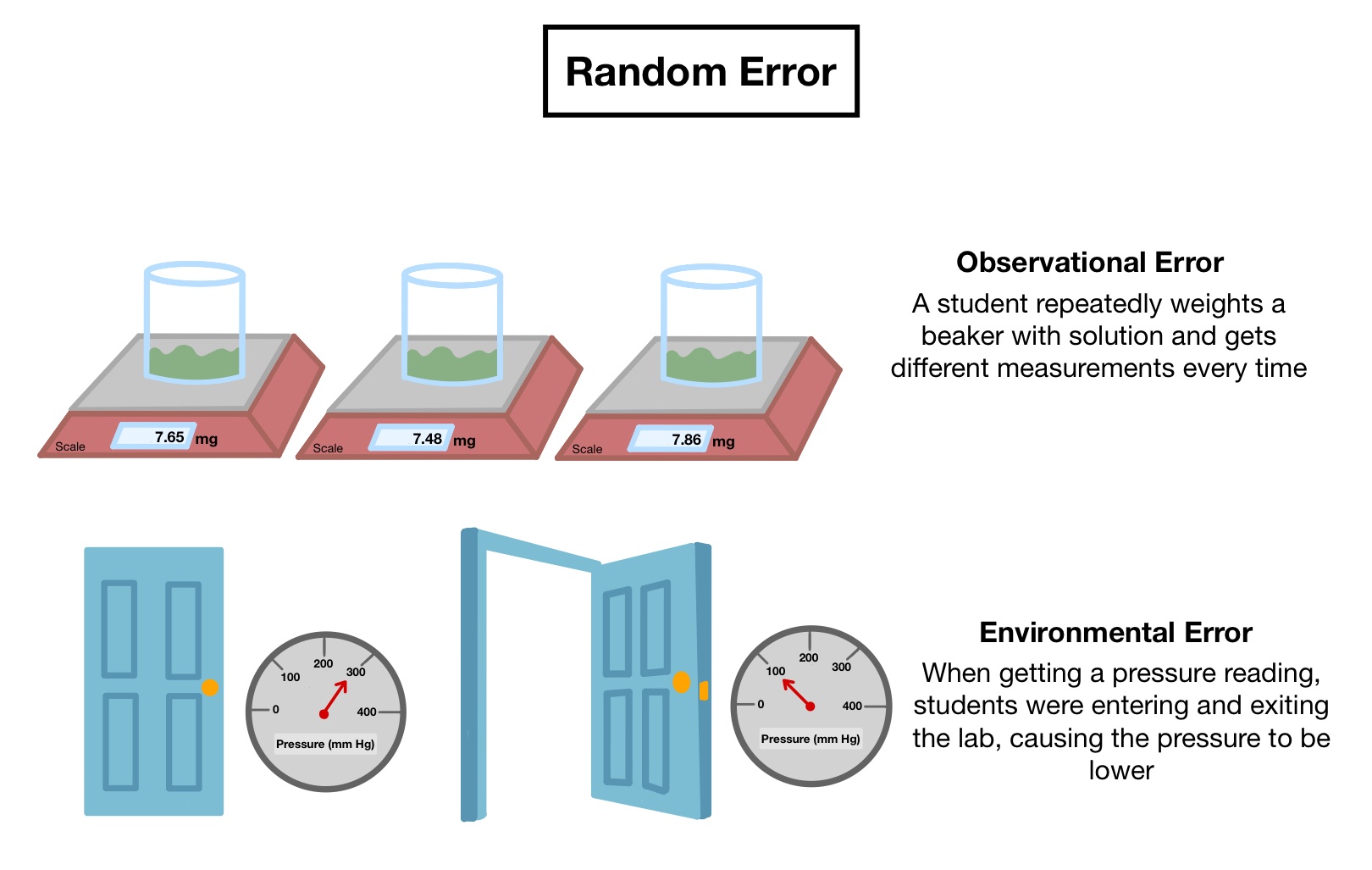
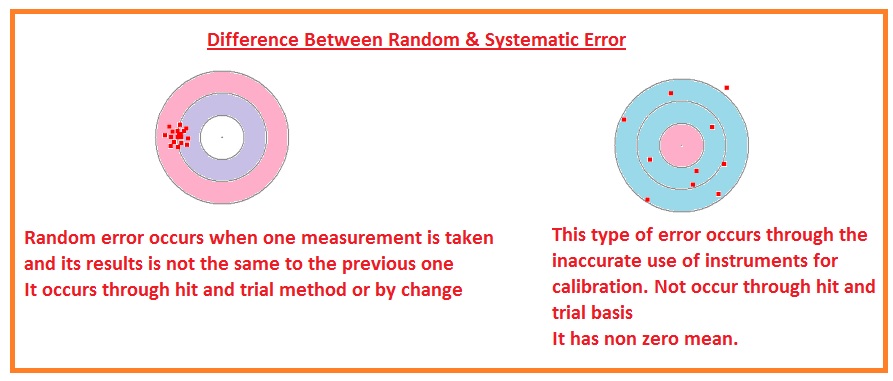
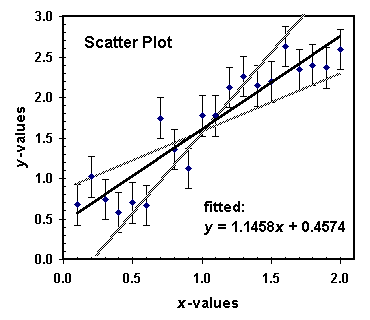
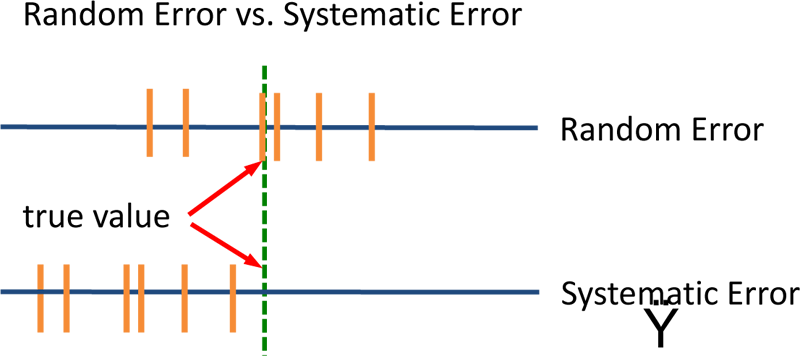
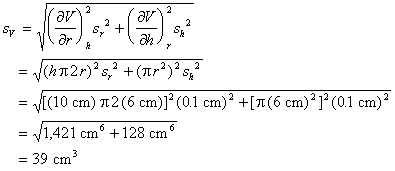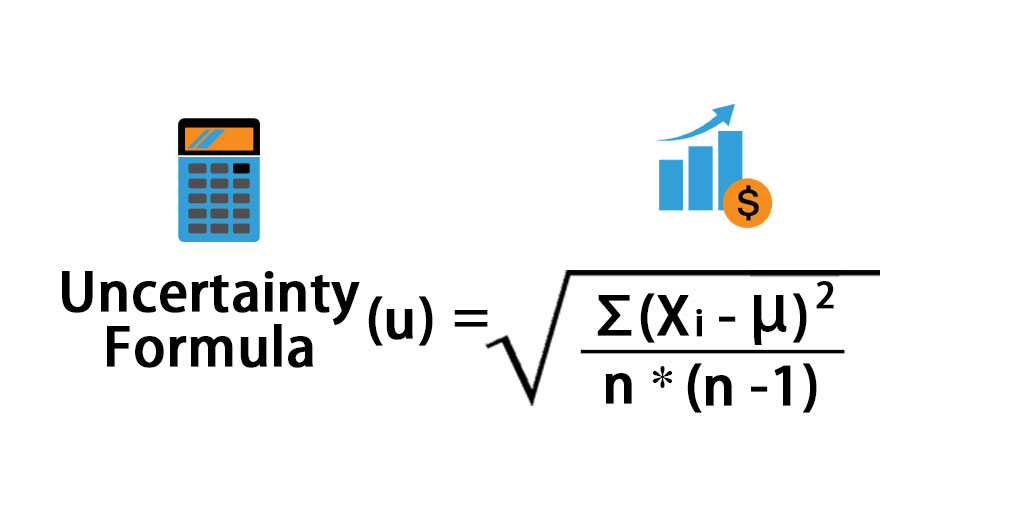The ± 1 second is called the absolute uncertainty Every measurement has an uncertainty or error. e.g. time = 5 seconds ± 1 second There are three main. - ppt download

The ± 1 second is called the absolute uncertainty Every measurement has an uncertainty or error. e.g. time = 5 seconds ± 1 second There are three main. - ppt download

Calculation of method error: systematic error was as- sessed using a... | Download Scientific Diagram